|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Cd40tm1(CD40)Bcgen Cd40lgtm1(CD40LG)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hCD40/hCD40L mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
121335
|
Related Genes
|
CD40 (Bp50, CDW40, TNFRSF5, p50)
CD40LG (CD154, CD40L, HIGM1, IGM, IMD3, T-BAM, TNFSF5, TRAP, gp39, hCD40L)
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
958,21947
|
mRNA expression analysis
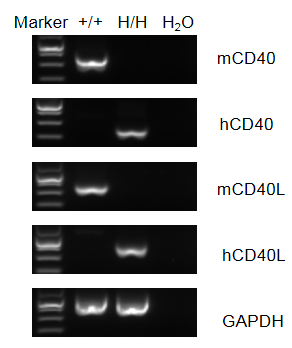
Strain specific analysis of CD40/CD40L gene expression in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and B-hCD40/CD40L mice by RT-PCR. Mouse CD40/CD40L mRNA was detectable in splenocytes of wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+). Human CD40/CD40L mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hCD40/CD40L (H/H), but not in wild-type mice.
Protein expression analysis
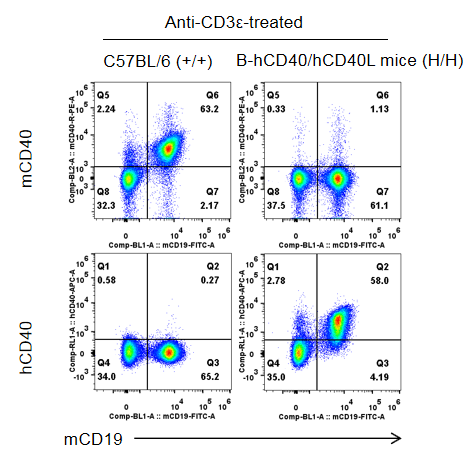
Strain specific CD40 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L mice (H/H) stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo (7.5 μg/mice, stimulation for 24 hours, i.p.), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD40 antibody. Mouse CD40 was detectable in wild-type mice. Human CD40 was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L but not in wild-type mice.
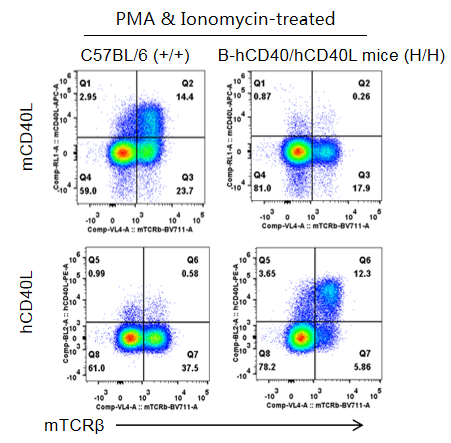
Strain specific CD40L expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L mice by flow cytometry. Thymocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L mice (H/H) and stimulated with PMA & Ionomycin, then analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD40L antibody. Mouse CD40L was detectable in wild-type mice. Human CD40L was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD40/hCD40L but not in wild-type mice.
In vivo efficacy of anti-CD40 and anti-CD40L antibodies
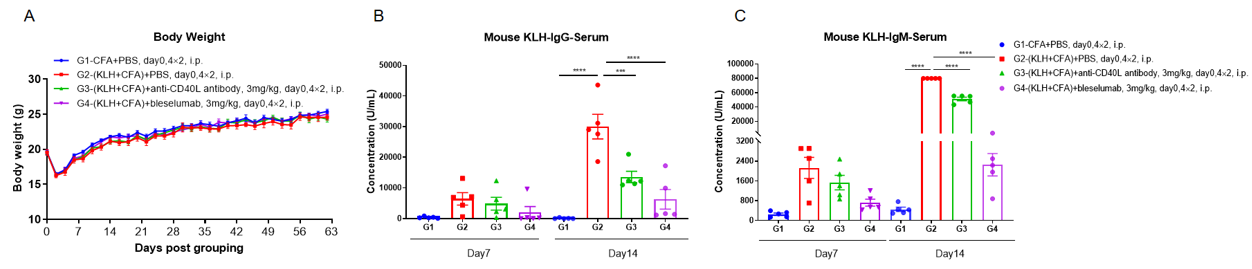
B-hCD40/hCD40L mice was used to establish The T-Dependent Antibody Response assay (TDAR assay) and evaluate the efficacy of anti-CD40 and anti-CD40L antibody. B-hCD40/hCD40L mice (n=5) were intraperitoneally immunized with 100 μg KLH on Day 1 and treated with anti-CD40L (provided by the client) or bleselumab (anti-CD40) (in house). Blood was collected on Day 7 and Day 14 and analyzed by ELISA with KLH specific IgG antibody and KLH specific IgM antibody. (A) Body weight of B-hCD40/CD40L mice increased steadily; (B, C) Concentration of mouse KLH specific IgG and IgM were significantly increased after immunization. But the concentration of KLH specific IgG and IgM in the groups treated with anti-CD40L antibody or bleselumab were significantly decreased when compared to that in the control group, demonstrating that the B-hCD40/hCD40L mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-CD40 and anti-CD40L antibodies.
Schematic of EAE model
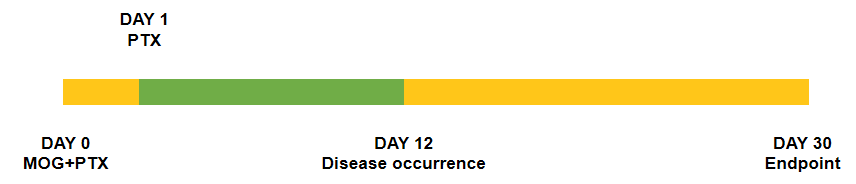
Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an induced demyelinating disease model that closely resembles the progression and symptoms of the human neurological disease Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
Clinical score of EAE model
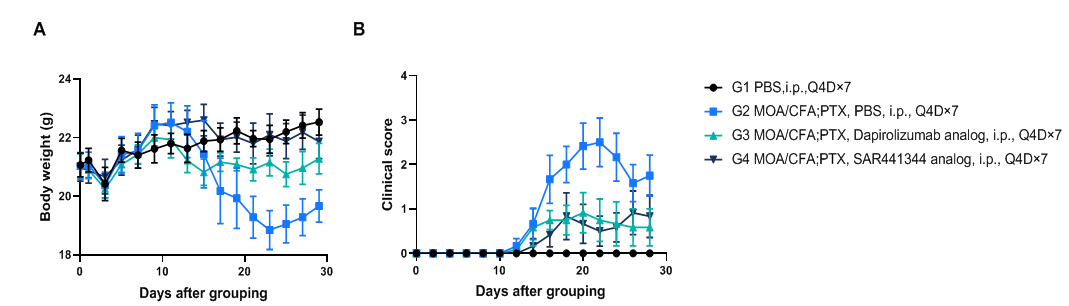
Effects of anti-CD40L (analog, in-house) on MOG35-55 induced EAE. B-hCD40/hCD40L mice (female, 11-week-old, n=6) immunized with MOG35-55 peptide (s.c.) were injected 2 times with PTX after immunization. Body weight (A) and clinical score (B) were recorded every two days. The results showed that compared with the control group (G1), MOG35-55 immunized mice (G2-G4) exhibited symptoms such as tail weakness, limping, hind limb paralysis and other symptoms, with a significant increase in clinical scores. This indicates that the EAE disease model was successfully induced in B-hCD40/hCD40L mice. After treating CD40L antibody drugs, a significant alleviation of clinical symptoms was observed. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
MOG: myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; PTX: pertussis toxin.
LFB and H&E staining in mouse EAE model
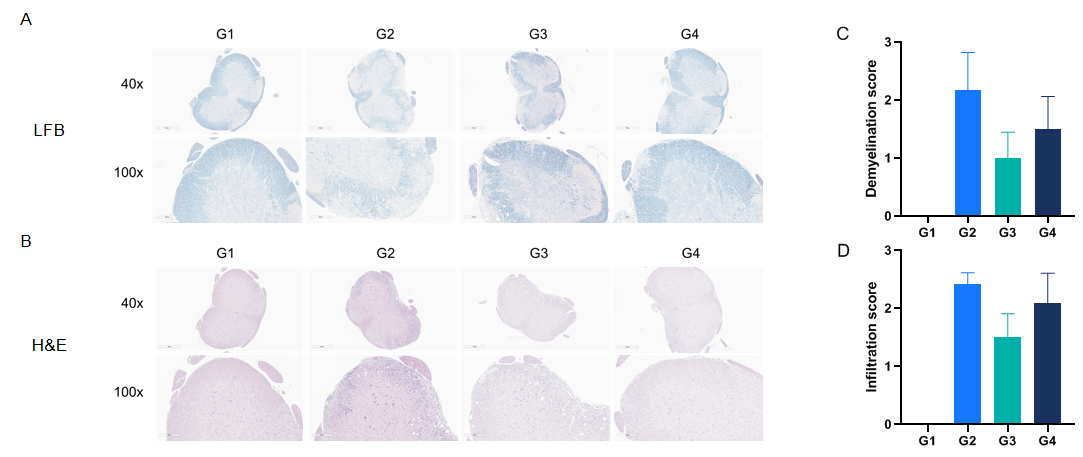
Anti-CD40L antibodies (analog, in-house) improves EAE clinical signs and controls inflammation and demyelination. Spinal cords were removed from B-hCD40/hCD40L mice on day 30 and stained with Luxol fast blue (LFB) (A) or Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (B). Representative sections are shown. The score of inflammatory cells and demyelination of spinal cord (C&D).

















 京公網安備: 11011502005564號
京公網安備: 11011502005564號