|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Pdcd1tm1(PDCD1)Bcgen Cd274tm1(CD274)Bcgen Sirpatm1(SIRPA)Bcgen Cd47tm1(CD47)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
140577
|
Aliases
|
CD279, PD-1, PD1, SLEB2, hPD-1, hPD-l, Hsle1, B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, PDL1, hPD-L1, B7DC, Btdc, CD273, PD-L2, PDCD1L2, PDL2, bA574F11.2,BIT, CD172A, MFR, MYD-1, P84, PTPNS1, SHPS1, SIRP, IAP, MER6, OA3
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
18566,60533,19261,16423
|
Protein expression analysis
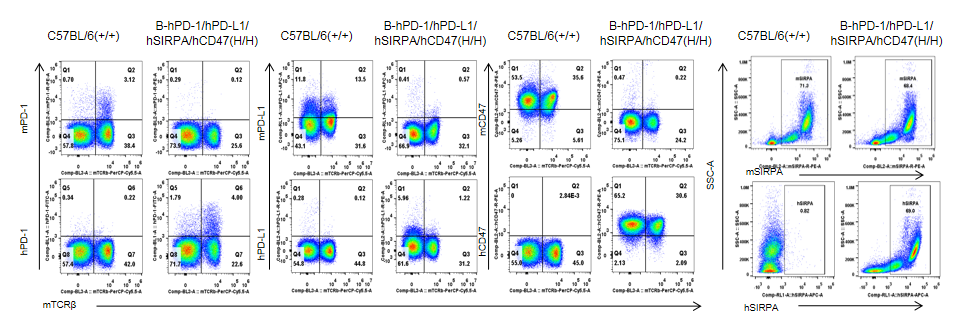
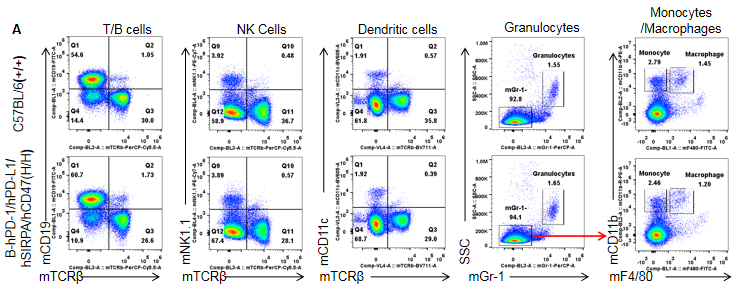
Strain specific PD-1, PD-L1, CD47 and SIRPα expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes from both wild type (+/+) C57BL/6 and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 (H/H) mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-1+, PD-L1 and CD47+ T cells were only detectable in the WT C57BL/6 mice. Human PD-1+, PD-L1+ and CD47+ T cells were only detectable in the homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in WT mice. This anti-mouse SIRPα antibody also cross reacts with hSIRPα. Human SIRPα was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice but not in WT mice.
Protein expression analysis
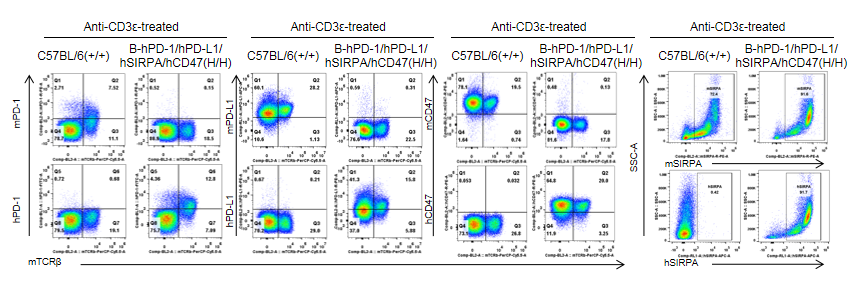
Strain specific PD-1, PD-L1, CD47 and SIRPα expression analysis in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes from both wild type (+/+) C57BL/6 and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 (H/H) mice were stimulated with anti-CD3ε in vivo and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mouse PD-1+, PD-L1 and CD47+ T cells were only detectable in the WT C57BL/6 mice. Human PD-1+, PD-L1+ and CD47+ T cells were only detectable in the homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. Mouse SIRPα was detectable in WT mice. This anti-mouse SIRPα antibody also cross reacts with hSIRPα. Human SIRPα was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice but not in WT mice.
Analysis of spleen leukocytes cell subpopulations in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47
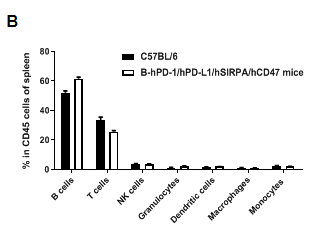
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS
Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for CD45 population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, monocytes, DCs, granulocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hSIRPα and hCD47 in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47a
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations by FACS
Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3 T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of CD8, CD4, and Treg cells in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hSIRPα and hCD47 in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
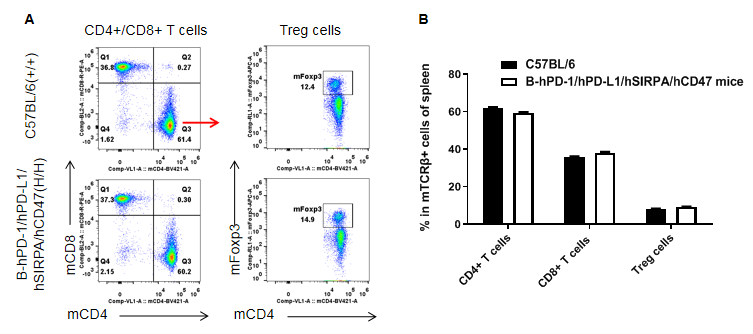
Analysis of lymph node T cell subpopulations in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47
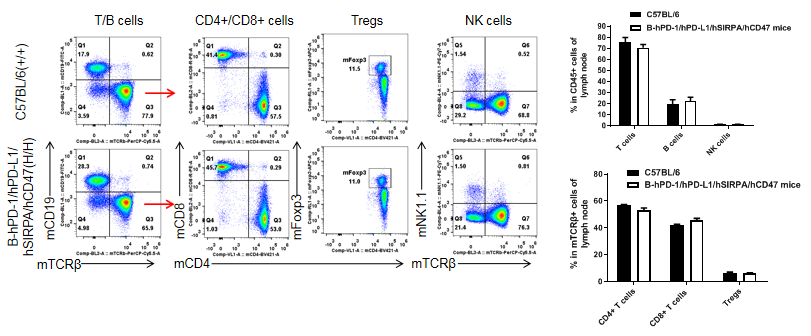
Analysis of lymph node T cell and NK cell subpopulations by FACS
Lymphocyte were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (n=3, 6-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the lymphocyte was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for TCRβ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of CD8, CD4, NK and Treg cells in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that introduction of hPD-1, hPD-L1, hSIRPα and hCD47 in place of its mouse counterpart does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
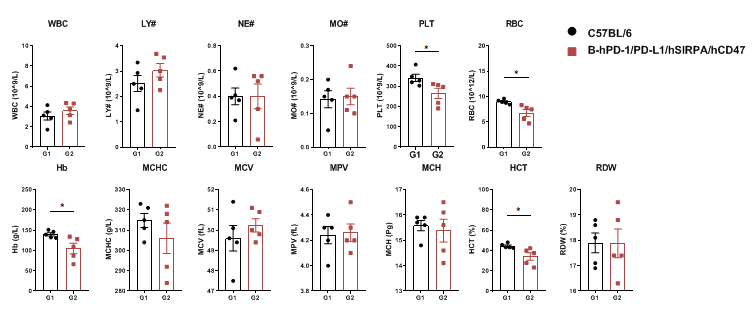
Blood routine test of B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice
Complete blood count (CBC)
Blood from female C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (n=5, 6 weeks-old) was collected and analyzed by CBC. Except PLT, RBC, Hb and HCT, C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice showed no difference in other test results. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
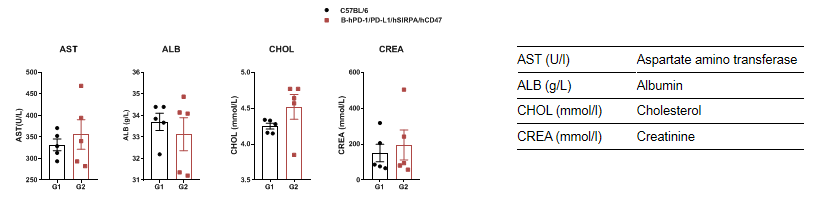
Blood chemistry of B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice
Blood chemistry tests of B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice
Serum from the C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 (n=3, 6 week-old) was collected and analyzed for levels of biochemistry. There was no differences on AST, ALB, CHOL, CREA measurement between C57BL/6 and B-hPD-1/hPD-L1 mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Combination therapy of anti-human PD-1 Ab and CD47 Ab
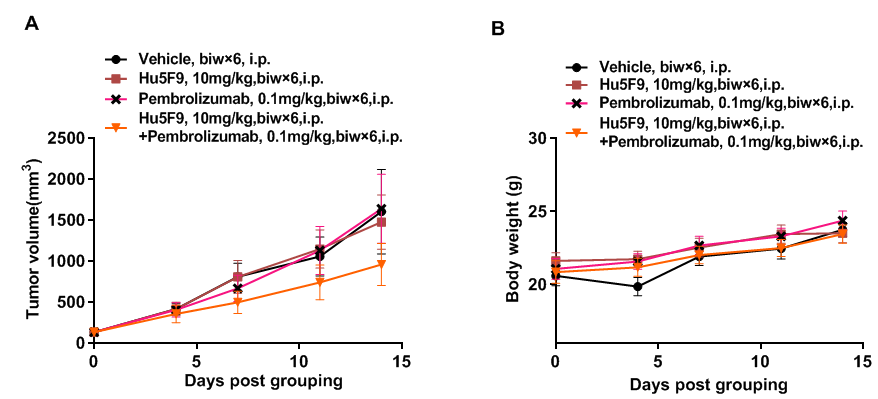
Antitumor activity of anti-human PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab (in house) combined with anti-human CD47 antibody Hu5F9 (in house) in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. (A) Pembrolizumab combined with Hu5F9 inhibited MC38-hPD-L1/hCD47 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. Murine colon cells (5E5) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (female, 8week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of pembrolizumab and Hu5F9 shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of combination therapy of anti-human PD-1 and anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Combination therapy of anti-human PD-L1 Ab and CD47 Ab
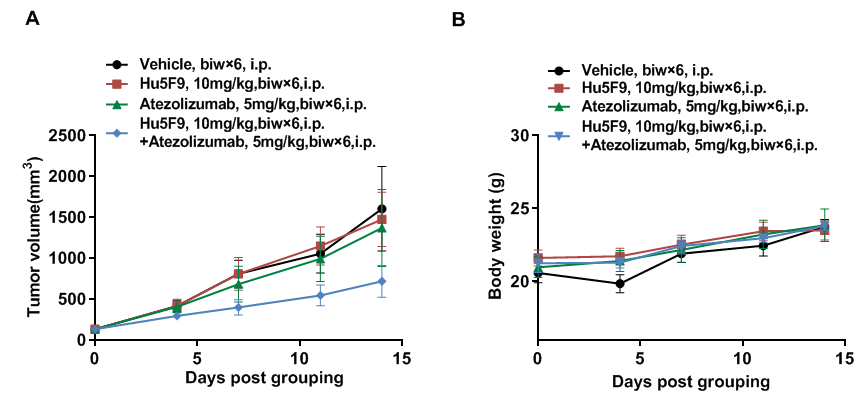
Antitumor activity of anti-human PD-L1 antibody Atezolizumab (in house) combined with anti-human CD47 antibody Hu5F9 (in house) in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. (A) Atezolizumab combined with Hu5F9 inhibited MC38-hPD-L1/hCD47 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. Murine colon cells (5E5) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (female, 8week-old, n=5). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 150 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of Atezolizumab and Hu5F9 shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of combination therapy of anti-human PD-L1 and anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Combination therapy of anti-human PD-1 Ab and CD47 Ab
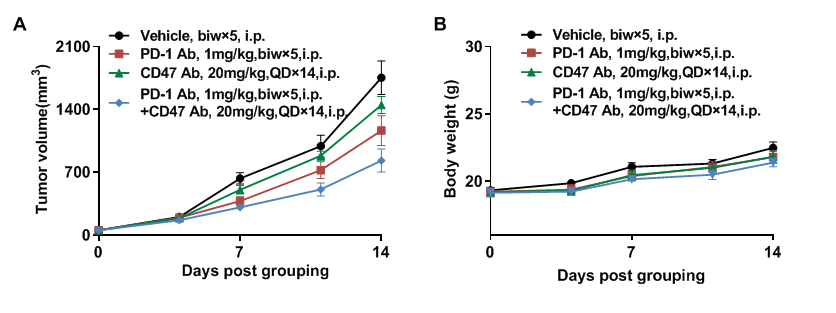
Antitumor activity of anti-human PD-1 antibody combined with anti-human CD47 antibody in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. (A) Anti-human PD-1 antibody combined with anti-human CD47 antibody inhibited MC38-hPD-L1/hCD47 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice. Murine colon cells (2E5) were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice (female, 6-8 week-old, n=8). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached 50-80 mm3, at which time they were treated with antibodies with doses and schedules indicated in panel A. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, combination of anti-PD-1 and anti-CD47 shows more inhibitory effects than individual groups, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hSIRPA/hCD47 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of combination therapy of anti-human PD-1 and anti-human CD47 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. PD-1 Ab and CD47 Ab are both provided by the clients)


















 京公網安備: 11011502005564號
京公網安備: 11011502005564號